Innate immunity and cell death in chronic lung diseases
Abstract
Chronic airway diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), are characterized by a complex inflammatory scenario, sometimes resistant to treatment with steroids and often associated with airway remodeling. Cigarette smoking is one of the main risk factors: it induces oxidative stress and tissue damage, and alters the innate immune response, generating chronic inflammation and increasing the risk of infection. By altering the processes of resolution of inflammation and promoting cell death, smoking favors the establishment of chronic inflammatory conditions following bacterial or viral infections.
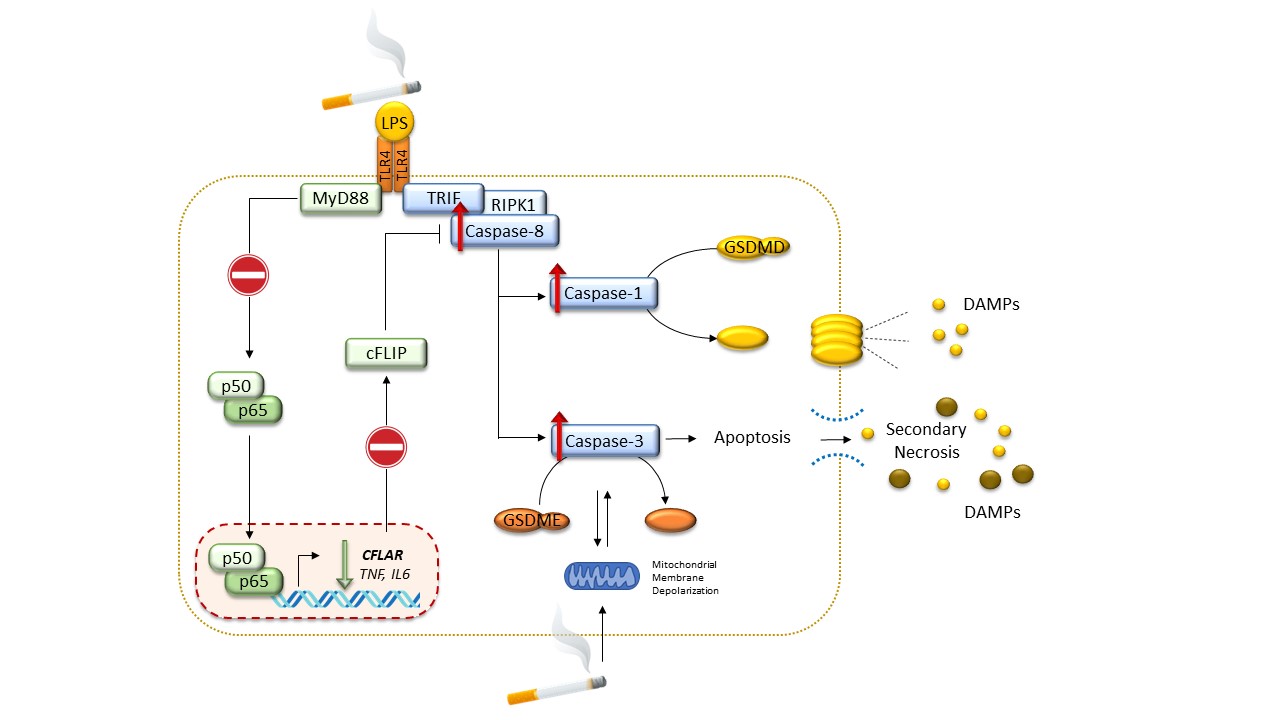
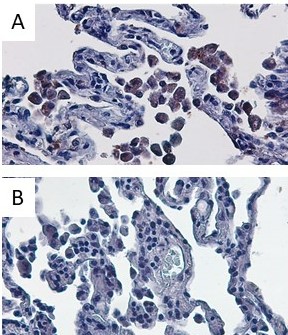
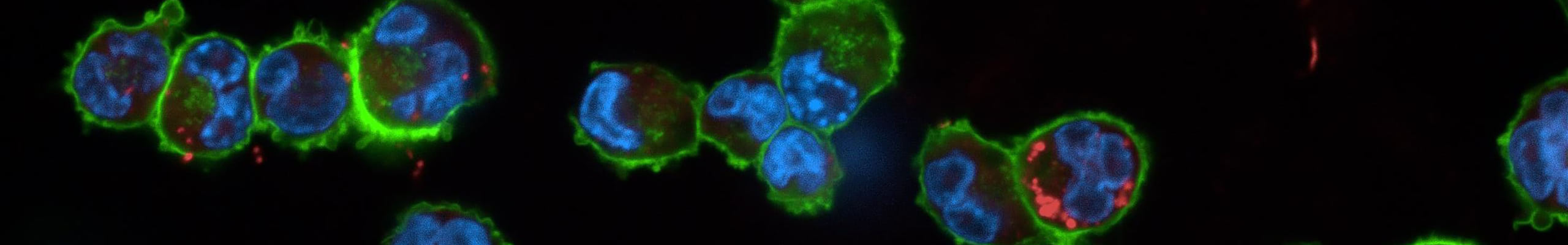
Alveolar macrophages play a pivotal role in orchestrating the innate immune response against external agents and pathogens, ensuring an effective host defense and activating the resolution of inflammation. Regulated cell death (such as pyroptosis, apoptosis, NETosis) has a key role in the regulation of inflammation. However, while it ensures an effective immune response, if not controlled can become a trigger for inflammatory responses that are harmful to the host.
Inflammasomes are multiprotein complexes composed by a receptor, an adapter protein, known as ASC, and pro-caspase-1. Inflammasome activation promotes autocatalytic cleavage of caspase-1, which in turn activates pro-IL-1β, pro-IL-18, and gasdermin D (GSDMD). Upon activation, GSDMD forms pores on cell membranes, allowing unconventional secretion of intracellular proteins and increasing permeability ultimately leading to pro-inflammatory pyroptosis.
Our study focuses on the role of inflammasomes and cell death: (i) in the pathogenesis of chronic lung diseases associated with cigarette smoking; (ii) in the response to viral infections.
We hypothesize that the activation of gasdermin in pulmonary myeloid cells, contributing to the release of damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) and eventually cell death, promotes steroid-resistant neutrophilic inflammation as well as the activation of pro-fibrotic pathways contributing to airways remodeling.
Pipeline
-
CLINICAL
NEED -
DISEASES
ANALYSIS - DISCOVERY
-
PRECLINICAL
VALIDATION -
PRECLINICAL
DEVELOPMENT -
CLINICAL
STUDIES
Responsabile Progetto
Contatto
Team di progetto:
Maria Rita Giuffrè
Agnese La Mensa, PhD
Lara Di Leonardo
Salvatore Caruccio
Aree terapeutiche:
Prodotto:
Farmaci – Biomarcatori
Collaborazioni:
- IRCCS ISMETT, Palermo, Italia;
- Istituto di Farmacologia Traslazionale (IFT)-CNR, Palermo, Italia;
- Istituto per la Ricerca e l’Innovazione Biomedica (IRIB) – CNR, Palermo, Italia;
- Dipartimento di Biomedicina, Neuroscienze e Diagnostica avanzata, Università Degli Studi di Palermo; Palermo, Italia;
- Azienda di Rilievo Nazionale ed Alta Specializzazione Ospedali (A.R.N.A.S) “Civico Di Cristina Benfratelli”, Palermo, Italia;
- University Medical Center Groningen (The Netherlands).
Scarica il pdf del progetto